
If the option expires worthless, there is no more cash flow from the trade and you keep all the initial cash, which is also your total profit. The maximum you can gain from a short put trade is the amount you receive at the beginning when selling the put. In this example we have sold one contract of a 45 strike put option for the price of 2.85 per share, which is $285 for one option contract representing 100 shares.
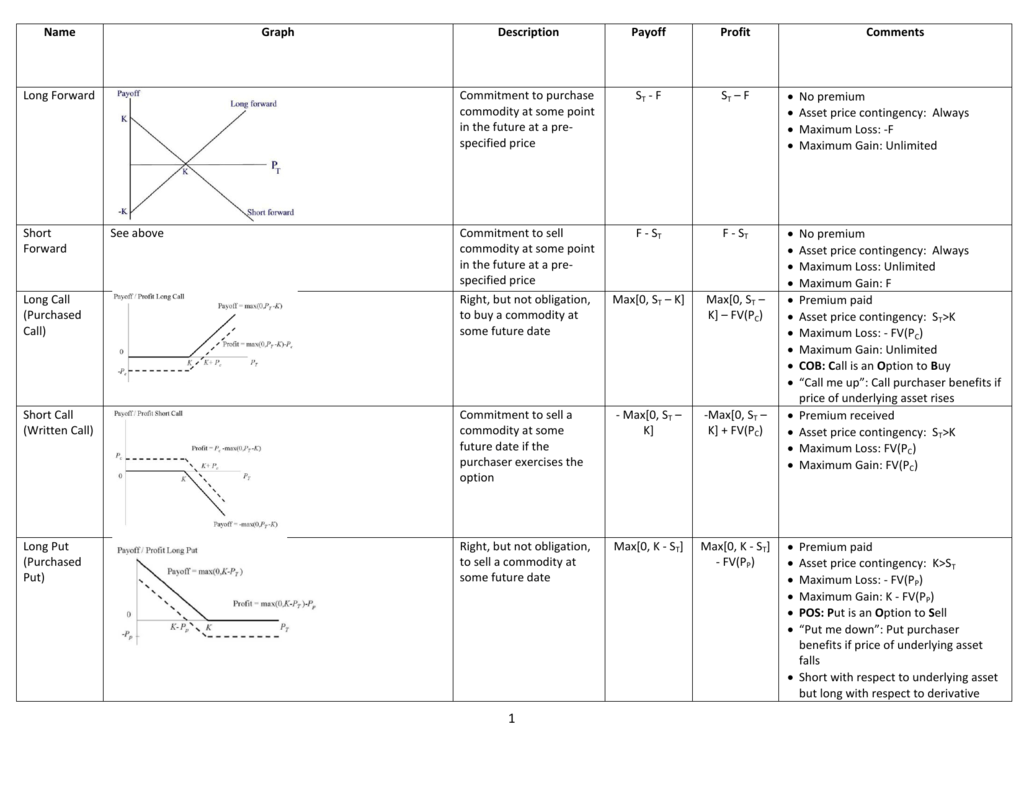
Let’s use the example from the screenshot above to explain the best and worst case scenario for a short put strategy. Below the strike price your profit declines in proportion with the underlying price. Maximum profit is reached when the underlying security ends up at or above the put option’s strike price and the option expires worthless. The payoff is inverse of long put position, which is the other side of your trade. Drawing Option Payoff Diagrams in Excel.Call, Put, Long, Short, Bull, Bear: Terminology of Option Positions.Essentially the option has expired worthless and has cost the buyer the initial premium. In the hands of the put buyer (long put), p T = 0 and Π = – p 0 or a loss of $3. Therefore p T = 0 and Π = p 0 which means profit = $3.
The put seller is short a put and the exercise price ($100) is less than the underlying price ($105) so we have a state where S T ≥ X. If a put option has a premium of $3 and the exercise price is $100 and the price of the underlying is $105, which reflects the value at expiration and the profit to the option seller? This means the maximum profit and maximum loss are interchanged for the buyer and seller, and the breakeven value remains the same. As a result, the option seller will have the converse payoff profile to the option buyer, and the sum of the positions of buyer and seller is zero.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
